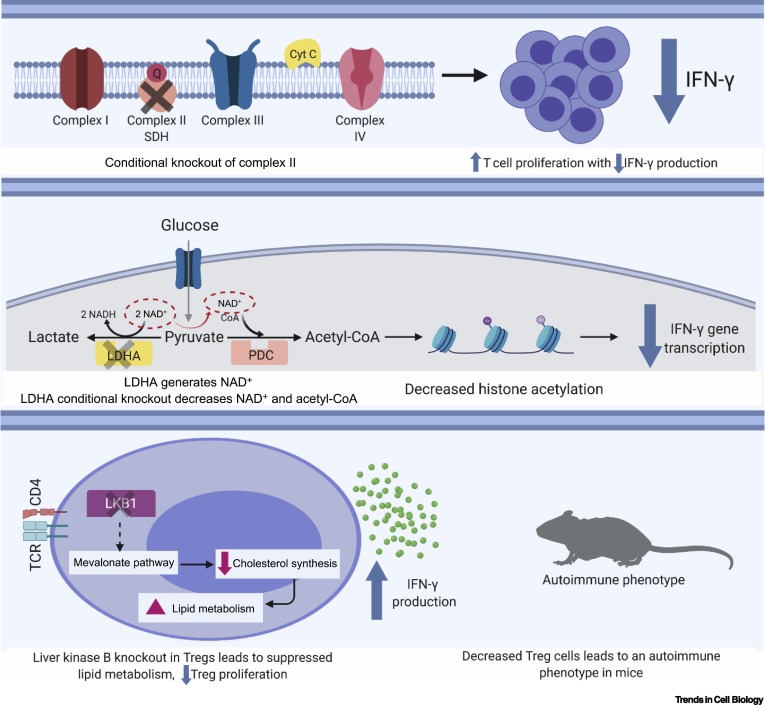
 Increasing evidence implicates metabolic pathways as key regulators of cell fate and function. Although the metabolism of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids is essential to maintain overall energy homeostasis, the choice of a given metabolic pathway and the levels of particular substrates and intermediates increasingly appear to modulate specific cellular activities. This connection is likely related to the growing appreciation that molecules such as acetyl-CoA act as a shared currency between metabolic flux and chromatin modification. We review recent evidence for a role of metabolism in modulating cellular function in four distinct contexts. These areas include the immune system, the tumor microenvironment, the fibrotic response, and stem cell function. Together, these examples suggest that metabolic pathways do not simply provide the fuel that powers cellular activities but instead help to shape and determine cellular identity.
Increasing evidence implicates metabolic pathways as key regulators of cell fate and function. Although the metabolism of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids is essential to maintain overall energy homeostasis, the choice of a given metabolic pathway and the levels of particular substrates and intermediates increasingly appear to modulate specific cellular activities. This connection is likely related to the growing appreciation that molecules such as acetyl-CoA act as a shared currency between metabolic flux and chromatin modification. We review recent evidence for a role of metabolism in modulating cellular function in four distinct contexts. These areas include the immune system, the tumor microenvironment, the fibrotic response, and stem cell function. Together, these examples suggest that metabolic pathways do not simply provide the fuel that powers cellular activities but instead help to shape and determine cellular identity.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0962892419302193?via%3Dihub
